With an out of the box configuration it is not possible to query SNMP or other similar services on the LAN interface address of a remote firewall running pfSense software over a tunnel mode IPsec VPN connection.
software over a tunnel mode IPsec VPN connection.
Fred Wright explained in a post to the m0n0wall mailing list on September 12, 2004 why this is, and it’s the same reason here.
"Due to the way IPsec tunnels are kludged into the FreeBSD kernel, any traffic initiated by m0n0wall to go through an IPsec tunnel gets the wrong source IP (and typically doesn’t go through the tunnel at all as a result). Theoretically this shouldn’t be an issue for the server side of SNMP, but perhaps the server has a bug (well, deficiency, at least) where it doesn’t send the response out through a socket bound to the request packet. You can fake it out by adding a bogus static route to the remote end of the tunnel via the m0n0wall’s LAN IP (assuming that’s within the near-end tunnel range). A good test is to see whether you can ping something at the remote end of the tunnel (e.g. the SNMP remote) from the m0n0wall. There’s an annoying but mostly harmless side-effect to this - every LAN packet to the tunnel elicits a no-change ICMP Redirect."
Most notably this is a problem for UDP services bound to all interfaces (*) and ICMP. In these cases, a reply uses the “closest” address to the client from the perspective of the system routing table. Without a route present matching the desired destination this results in using the IP address of the interface containing the default gateway.
Service Binding Workaround¶
Some services have options which make it possible to change the interface binding so that the daemon only binds to a specific interface or IP address (e.g. the IP address of the internal network on the local end of the VPN) on the firewall. The interface binding for SNMP, NTP, the DNS Forwarder, and several other services can be set in this way.
With the daemon bound to only that specific address, that is also the only address it can use to reply, and thus it can generate the expected replies which will properly take the IPsec path back to the other end.
Static Route Workaround
If changing the service binding is not possible, or for full connectivity between the endpoints, use static routes to work around the situation.
Note:
When both endpoints must be accessed, a static route is required on each endpoint.
Setting up a static route is done by first adding a gateway pointing to the LAN IP address of the firewall and then adding a static route using this gateway.
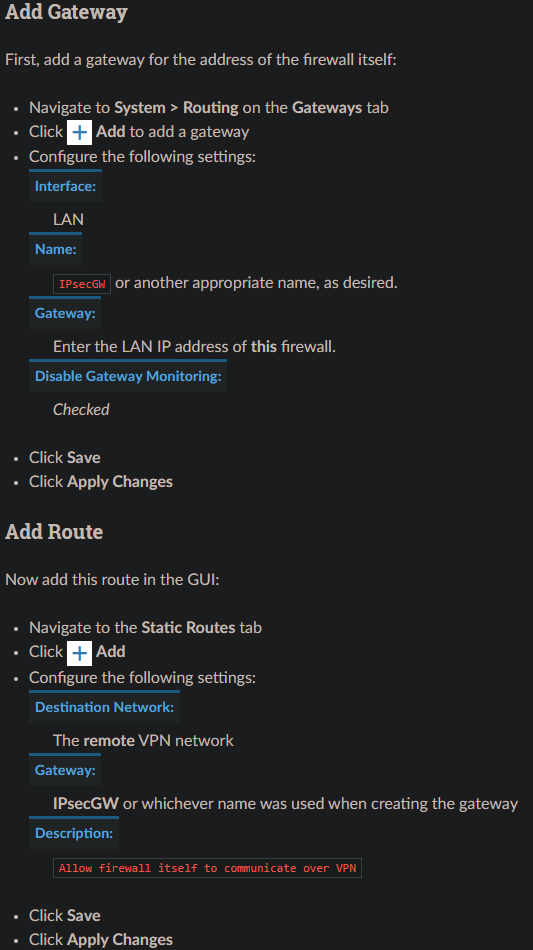
Test
Perform a test using the address of the far side system and the local address that system is attempting to query.
Routed IPsec (VTI)
The previous advice in this document does not generally apply to route-based IPsec (VTI mode) since it operates in a fundamentally different way than policy-based IPsec (tunnel mode).
With VTI mode IPsec the routing table contains proper routes back to the remote end using the VTI interfaces. Responses will utilize these routes to select the IPsec interface when looking up the path back across the tunnel.
This may mean the remote end should query the address of the IPsec interface directly so that the responses are received from a matching address, but whether or not this is necessary depends on the service and client.
 software over a tunnel mode IPsec VPN connection.
software over a tunnel mode IPsec VPN connection.